IntroductionPetals CLI is a command line client to administrate a set of Petals nodes.
To work, Petals CLI needs to establish a connection with a Petals node.
Usage of Petals CLI
usage: Petals JMX Command Line Interface
[-d] [-y] [-h <host> -n <port> | -h <host> -n <port> -u <user> -p <password> | -a
<alias>] [-H | -V | [--file] <filename> | -c -- <command> | -C]
-a,--alias <alias> Connection alias in the preference file.
-c,--command Execute a command given on the command line after '--'.
-C,--console Enable the mode 'console'.
-d,--debug Print stack trace and debugging informations
--file <filename> Enable the script file execution. If filename is '-',
commands are read from the stdin.
-H,--help Print this help message and exit.
-h,--host <host> JMX host of the remote petals ESB.
-n,--port <port> JMX port of the remote petals ESB.
-p,--password <password> JMX password of the remote petals ESB.
-u,--user <user> JMX user of the remote petals ESB.
-V,--version Print the version number and exit.
-y,--yes Enable automatic confirmation ('yes' flag)
Which evolution would you like on Petals? Share it! http://www.petalslink.com/feedback
To get available commands, use the command 'help' on command-line: petals-cli.sh -c – help
Available commands:
connect Connect to a Petals ESB node.
deploy Deploy and start a JBI artifact.
disconnect
Disconnect from a petals container.
exit Exit this shell.
help Display this help message or help for a specific command.
list List JBI artifacts name and current status.
load Load properties from files.
logger-set
Set the specified level to the specified logger.
loggers Return all the loggers.
print Print a message.
properties-list
Get the values defined in its server.properties file.
pwd Print the working directory.
registry-list
List the entries of the registry.
registry-sync
Synchronize the registry.
set Assign a value to the system property named key.
show Print informations about a JBI artifact.
start-artifact
Start a JBI artifact.
stop Stop the container.
stop-artifact
Stop a JBI artifact.
system Execute system command.
topology-list
Get information about the topology this node is part o.
undeploy Stop and uninstall or undeploy JBI artifacts.
version Print version informations about petals container.
For help on a specific command type:
help <command>
To get help on a command, use the command 'help' on command-line: petals-cli.sh -c – help <command>
|
Table of contents
Contributors
No contributors found for: authors on selected page(s)
|
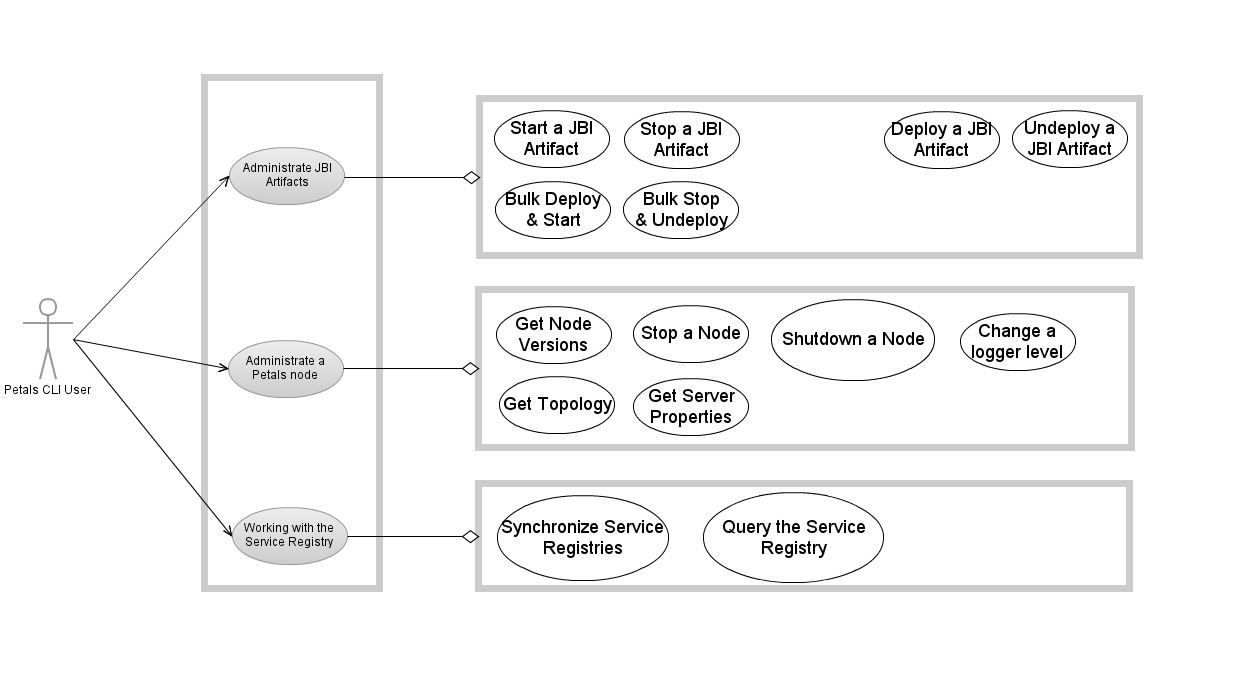
Use Cases
|
Petals CLI: the Basis
Installing Petals-CLI
The installation of Petals CLI depends on your operating system. The following table resumes which archives is needed according to your operating system. Petals CLI archives are available on the Petals's web-site: http://download.petalslink.com/petals-esb.html.
| Operating System | OS Version | Petals archive to use | Installation procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Debian-based Linux | all | Debian packages | Installing Petals CLI using the Debian packages |
| Linux | all | ZIP archive | Installing Petals CLI using the ZIP archive |
| Microsoft Windows | all | ZIP archive | Installing Petals CLI using the ZIP archive |
| Mac OS | all | ZIP archive | Installing Petals CLI using the ZIP archive |
Note: The ZIP archive can be used on Debian-based systems. In this case, Petals CLI should be installed as a user software without integration with the operating system.
Petals CLI capabilities about script and shell usages
Interactive console
Launching Petals CLI with the following command line starts an interactive console with a prompt where the user can enter commands.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C
Type 'help' for help.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
petals-cli>
On Windows, to be able to launch Petals CLI by a double-click, this command is wrapped by another script: petals-cli-console.bat.
On Linux, there is no wrapper script but a shell alias can be created.
Execution of a Petals CLI command directly on the command line
Launching Petals CLI with the following command line executes the command specified on the command line.
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- <command> <command-args>
Execution of a Petals script file
Launching Petals CLI with the following command line executes the commands from the specified Petals script.
> ./petals-cli.sh <filename> > ./petals-cli.sh --file <filename>
| A Petals script is text file containing commands supported by Petals CLI, and comments. Comments start by '#', optionally preceded by space(s). |
Execution of an inlined Petals script
Launching Petals CLI with the following command line executes commands provided through the standard input ("stdin").
> cat <filename> | ./petals-cli.sh - > cat <filename> | ./petals-cli.sh --file - > ./petals-cli.sh - << EOF <command1> <command1-args> <command2> <command2-args> EOF > ./petals-cli.sh --file - << EOF <command1> <command1-args> <command2> <command2-args> EOF
Getting help
Getting help on command line options and arguments
The help on command line options and arguments is available through the '-H' option. A text containing options, arguments and available commands is displayed according to the usage defined above.
> ./petals-cli.sh -H
Getting help on commands from the command line
The help on a command is available by using the command 'help'. A usage and a description of the command is displayed:
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- help <command> usage: <command> <command-arguments> <command description> >
where:
- <command> is the command for which we want to get help.
- <command-arguments> is the list of arguments for the command.
- <command-description is a description of the command.
Getting help on available commands and on a command in interactive mode
The list of available commands is available by using the command 'help' without argument.
Help about a command is available by using the 'help' command. Command's usage and description are then displayed.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> help Available commands: deploy Deploy and start a JBI artifact in petals container. exit Exit this shell. help Display this help message or help for a specific command. ... For help on a specific command type: help <command> petals-cli> help <command> usage: <command> <command-arguments> <command description> petals-cli>
where:
- <command> is the command for which we want to get help.
- <command-arguments> is the list of arguments for the command.
- <command-description is a description of the command.
Getting the version of Petals CLI
To get the version of Petals CLI, the version of the JVM running Petals CLI, and its operating system, use the '-V' option:
> ./petals-cli.sh -V Petals JMX Command Line Interface 1.1.0-SNAPSHOT Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 1.6.0_26-b03 Linux 3.0.0-16-generic-pae
Working with variables
Petals CLI supports variables as properties. A variable is a placeholder with a name: ${variable-name}, that is replaced by its value when evaluating the command in which it is used.
connect -h ${host.name} -n ${host.port} -u ${host.user} -p ${host.password}
Listing available variables
The command 'set' without argument lists all available variables:
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> set ... java.runtime.name=Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment java.runtime.version=1.6.0_45-b06 java.specification.name=Java Platform API Specification java.specification.vendor=Sun Microsystems Inc. java.specification.version=1.6 ...
Setting a variable as property
A property can be set using the command 'set':
set [ property-name = property-value ]
set [ property-name =: property-value ]
set [ property-name : property-value ]
> ./petals-cli.sh -C
Type 'help' for help.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
petals-cli> set my-property-name=value
Return codes of Petals CLI
Return code on error parsing mode options
If Petals CLI is not able to determine the mode (interactive, scripting, executable or redirection) to use from arguments, the return code will be 1.
Return code of Petals CLI launched in interactive mode
Petals CLI launched in interactive mode will exist always with the return code 0, even if error occurs executing a command.
If an error occurs during a command execution or parsing:
- The error message is displayed.
- Petals CLI is not interrupted, the user can enter other commands.
Return codes of Petals CLI launched in executable mode
Return code on parsing error of the command arguments
When there is an error about options and arguments of the command, the return code of Petals CLI is 1.
Return code on command execution
When there is an error about the command execution, the command is interrupted and the return code of Petals CLI is 2.
Return code on successful command execution
When there is no error about options, arguments and execution of a the command, the return code of Petals CLI is the return code of the command
Return code of commands
All commands return the return code 0 when the execution succeeds, and 1 when the execution fails. Except the command 'system' that returns the return code of the system command invoked.
Return codes of Petals CLI launched in scripting modes
Options and arguments parsing of command
When using the script mode or inlined mode, parsing errors (invalid options and/or arguments) result in an interruption of Petals CLI.
The return code 1 then pushed back.
Error management of a command read from stdin or a file
If an error occurs during the execution of a flow of commands:
- The command that has thrown the error is interrupted.
- The return code of the command can be checked using the commands isParsingErrorReturned, isExecutionErrorReturned, isNoErrorReturned, the ternary conditional operator, and the lastErrorCode attribute.
> ./petals-cli.sh - << EOF deploy <artifact-url> isNoErrorReturned ? listartefacts : exit lastErrorCode EOF
Note:
- The return values of command isParsingErrorReturned, isExecutionErrorReturned and isNoErrorReturned are reset when invoking another command. Only the error of the last command execution can be checked.
- The attribute lastErrorCode is an argument of the command exit to return the return code of the last executed command.
Exit from the Console mode
To exit the console mode, use the 'exit' command.
If a number is set as an argument, it is used as return code. Otherwise, the 0 is returned.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> exit > echo $? 0 > ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> exit 1 > echo $? 1
| If an asynchronous command is running, the command 'exit' will wait the end of these pending commands to really exit. If you have infinite asynchronous command as defect subscription, you can force to exit using Ctrl+C or kill the processus. |
Petals CLI Preferences
It is possible to define preferences in Petals CLI. The preferences are defined in a properties file, as key/value pairs. Two levels of preference files are defined:
- a user level, by the file $HOME/.petals-cli/petals-cli.default
- and a system level. The location of this file is defined accordingly to the operating system:
OS/Distribution System level file Linux/Debian-based distribution /etc/petals-cli/petals-cli.default Windows %PETALS_CLI_HOME%\conf\petals-cli.default
If the user preference file exists, it is used. Otherwise the system preference file is used
| If Petals CLI is installed through the ZIP archive, and no user level file exists, it is possible to define another preference file through the environment variable $PETALS_CLI_PREFS. |
The preferences files contain a set of keys in several sections:
- section 'Global preferences':
- alias.default: the default alias to use (required).
- user.lang: the language to use in Petals CLI.
- This property is optional. If not set, OS settings are used. If the OS language setting is not supported, then English is used.
- If the value is specified and not supported, then English is picked up.
- French and English are the two languages that must be supported. Others are optional (but contributions are welcome).
- embedded.http.port: the listening port of the embedded HTTP server (see the command deploy). Default value: 7500.
- section defining aliases. An alias identifies all the properties of a connection. An alias is defined as following:
- <alias>.host: the host of the default Petals node (required).
- <alias>.port: the JMX port of the default Petals node (required).
- <alias>.username: the JMX user name for the default Petals node (optional).
- <alias>.password: the JMX password for the default Petals node (optional).
- <alias>.passphrase: the security passphrase to access critical information or execute critical operation on other Petals nodes (than the one on which Petals CLI is connected) of the topology (optional).
When optional keys are not defined, Petals CLI will ask for their values manually (or you will have to use the right options with the commands).
If the file does not exist, or that $PETALS_CLI_PREFS points to an invalid location, Petals CLI will use default settings when possible. Otherwise, it will display an error message.
For a server, the user and password must both be set or both be absent.
An error message is displayed if only one of them is specified.
The server alias must be unique in the properties file.
If a server alias is used twice, an error message will be displayed.
Initial content of the file:
# The default server / connection alias.default = default # The connection properties of the 1st server default.host = localhost default.port = 7700 default.username = petals default.password = petals default.passphrase = petals
Petals CLI extensions
Several Petals CLI extensions are available, they comes with new command(s):
| You can write your own command |
Connection to a Petals node
Connection options from the command line
All the required parameters for a JMX connection must be configurable on the command line as options:
> ./petals-cli.sh -h <host> -n <port> -u <user> -p <password> -c -- <command> > ./petals-cli.sh -h <host> -n <port> -u <user> -p <password> -C petals-cli@<host1>:<port1>>
An alias can also be used.
> ./petals-cli.sh -a <alias> -c -- <command> > ./petals-cli.sh -a <alias> -C petals-cli@<host1>:<port1>>
Interacting with several Petals nodes without exiting Petals CLI
In interactive mode or script mode, we should be able to close a connection and open another one without leaving Petals CLI. This is achieved with the 'connect' and 'disconnect' commands. If no argument is set on the 'connect' command, default values are used. These default values are specified in the preferences file. If a connection already exists, the 'connect' command will realize a disconnection before to establish the new connection.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> connect -h <host1> -n <port1> -u <user1> -p <password1> Connected on <host1>:<port1> with '<user1>' petals-cli@<host1>:<port1>> disconnect petals-cli> connect -a <alias> Connected on <host1>:<port1> with '<user1>' petals-cli@<host1>:<port1>> disconnect petals-cli> connect -h <host2> -n <port2> -u <user2> -p <password2> Connected on <host2>:<port2> with '<user2>' petals-cli@<host2>:<port2>> connect petals-cli@<host2>:<port2>> Would you like to connect to <default-user>:*****@<default-host>:<default-port>? (y/n) y petals-cli@<default-host>:<default-port>>
Default connection
By default (if no argument or option is set).
In console mode, the connection is established, by the command 'connect', with the values given in the preferences file.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> connect petals-cli> Would you like to connect to <default-user>:*****@<default-host>:<default-port>? (y/n) y petals-cli@<default-host>:<default-port>>
The confirmation can be skipped by adding the 'yes' argument to the command.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> connect -y petals-cli@<default-host>:<default-port>>
In command line mode, if no argument or option is set, a connection is automatically established (the command 'connect' is automatically executed before the provided command) with the values defined in the preferences file.
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- stop
| This is necessary to easily stop a local container |
In script mode, the connection is established, by the command 'connect', with the values defined in the preferences file.
> ./petals-cli.sh - << EOF connect EOF
If the preferences file does not exist and that connect was invoked without an argument, the command returns the error code 2.
Security
For security reasons, a Petals CLI user may decide that there should be no default connection.
In that case, he may decide to delete the preference file, so that any user will have to type in the right information.
If the preference (properties file) does not exist, Petals CLI displays an error message.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> connect No default connection is available. Use 'help connect' for more information.
Another possibility is that the user allows to record a default host and port but not the credentials.
In that case, Petals CLI will ask the user to type in the credentials.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> connect petals-cli> Would you like to connect to <default-host>:<-default-port>? (y/n) y petals-cli> Username: wrong-username petals-cli> Password: right-pwd Invalid credentials. petals-cli> Retry? (y/n) y petals-cli> Username: right-username petals-cli> Password: wrong-pwd Invalid credentials. petals-cli> Retry? (y/n) y petals-cli> Username: right-username petals-cli> Password: right-pwd petals-cli@<default-host>:<-default-port>>
Error Messages
| Error messages should be written in active form. Negative forms should be avoided. |
The preferences file does not exist.
The connect command results in the following error message.
No default connection is available. Use 'help connect' for more information.
The preferences file is invalid (missing property, or duplicate alias...).
The connect command results in the following error message.
The preferences file contains <N> error(s).
- Error 1
- Error2
Duplicate Alias.
The alias '<alias>' can only be used once.
Missing property.
The property '<property>' is missing.
Only user was specified for a server.
The credentials for '<alias>' are invalid: add the password or remove the user.
Only password was specified for a server.
The credentials for '<alias>' are invalid: add the user or remove the password.
Administration Commands
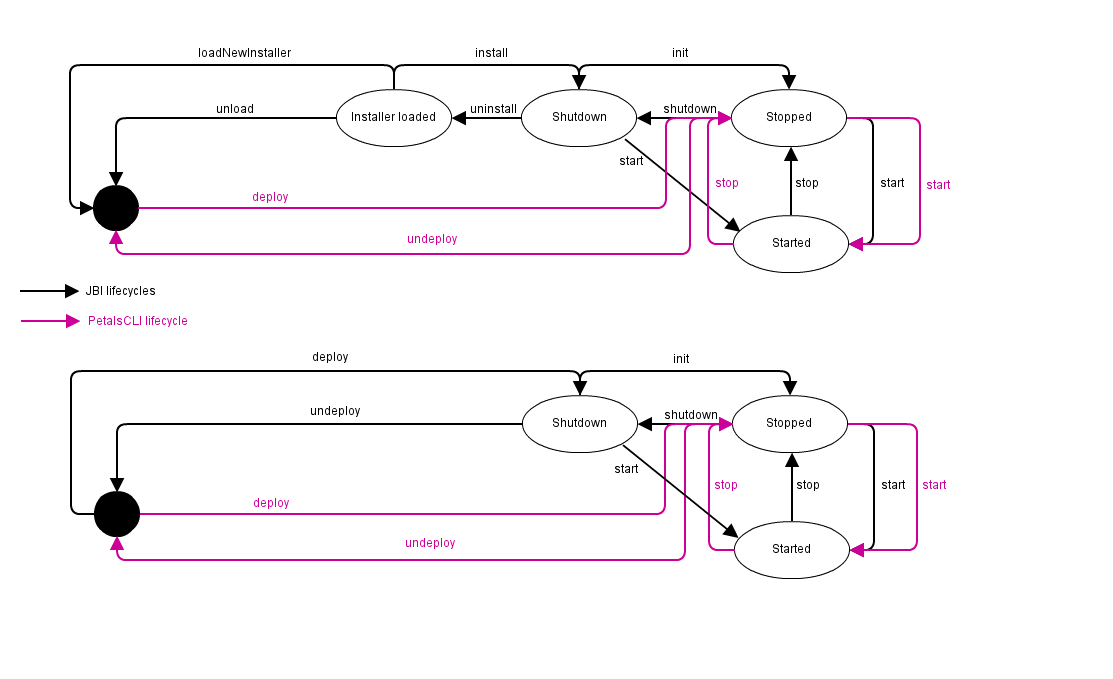
Working with JBI artifacts
Artifact lifecycle managed by PetalsCLI
|
Deploying and Starting an Artifact at once
Petals CLI is able to deploy and start a JBI artifact without distinction between shared-library, component and service assembly using the following command:
deploy -u <artifact-file> [-f,--file <configuration-file> | -D <configuration-properties>]
where:
- <artifact-file> is the local file name or the URL of the artifact to install or deploy and start
- <configuration-file> is the local file name or the URL of the properties file used to configure the artifact. This argument is used only if the artifact is a component. It has no sense for other artifacts. This argument is exclusive with <configuration-properties>.
- <configuration-properties> is a list of '<property-name>=<property-value>', separated by a comma, where <property-name> is the name of the property to configure with <property-value>. This argument is used only if the artifact is a component. It has no sense for other artifacts. This argument is exclusive with <configuration-file>.
| Auto-completion is available on artifacts identifiers and artifact file names. |
The command deploy is able to deploy an artifact local to Petals CLI on a remote Petals ESB container. An artifact is local to Petals CLI if deployed using a file or an URL with the protocol 'file'. In this case, the command deploy uses an embedded HTTP server. So the remote Petals ESB container will be able to download the artifact to deploy from Petals CLI. See Petals CLI preferences to configure the embedded HTTP server.
If the artifact to deploy is:
- a component:
- if its component installer is already loaded (the component is not installed), then the command 'deploy' will unload the component installer, reload a new one and continue the lifecycle (configuration, installation and start),
- if the component is installed:
- if the component is shutdown, then the command 'deploy' will uninstall the component, unload the component installer, reload a new one and continue the lifecycle (configuration, installation and start),
- otherwise an error occurs, use command 'undeploy' to fix it.
- a service assembly:
- if the SA is already deployed and in state 'SHUTDOWN', then the command 'deploy' will undeploy the service assembly, before to re-deploy a new one,
- otherwise an error occurs, use command 'undeploy' to fix it.
Deployment of an Artifact located in a Maven repository
| Not available. Coming soon ! |
Petals CLI is able to deploy and start a JBI artifact located into a Maven repository by using the following command:
deploy <maven-artifact> [<configuration-file> | <configuration-properties>]
where:
- <maven-artifact> is the Maven identifiers of the artifact to install: group-id:artifact-id:version[:classifier]. If required, the Maven repository can be defined in the Maven configuration file ($HOME/.m2/settings.xml)
- <configuration-file> is the local file name or the URL of the properties file used to configure the artifact. This argument is used only if the artifact is a component. It has no sense for other artifacts. This argument is exclusive with <configuration-properties>.
- <configuration-properties> is a list of '<property-name>=<property-value>', separated by a white character, where <property-name> is the name of the property to configure with <property-value>. This argument is used only if the artifact is a component. It has no sense for other artifacts. This argument is exclusive with <configuration-file>.
Same remarks about lifecycle of the deployment from an URL are applicable for the deployment from a Maven artifact.
Bulk Deployment and Start
To deploy and start several artifacts in one command, just put them in a local directory and execute the command 'deploy':
deploy -b,--bulk <url|file>
> ./petals-cli.sh -y - << EOF deploy -b file:///tmp EOF > ./petals-cli.sh -C Type 'help' for help. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ petals-cli> deploy -b /tmp
If the argument <artifact-file> of the 'deploy' command is a local directory, all artifacts of the directory are deployed.
| Only the protocol 'file' is available. |
Starting an Artifact
An artifact can be started by using the 'start-artifact' command:
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- start-artifact [ -u <artifact-file> | -a <artifact-id> [<artifact-type>] ]
where:
- <artifact-file> is the local file name or the URL of the artifact to start.
- <artifact-type> is the nature (SL, component, SA) of the artifact to start.
- <artifact-id> is the JBI identifier of the artifact to start.
| Auto-completion is available on artifacts IDs and artifact file names. |
If the artifact to start is a component or a service assembly, the command 'start-artifact' will succeed only if the artifact state on Petals ESB side is 'STOPPED' or 'SHUTDOWN', otherwise on error will occur.
Stopping an artifact
An artifact can be stopped by using the command 'stop-artifact':
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- stop-artifact [ -u <artifact-file> | -a <artifact-id> [<artifact-type>] ]
where:
- <artifact-file> is the local file name or the URL of the artifact to stop.
- <artifact-type> is the nature (SL, component, SA) of the artifact to stop.
- <artifact-id> is the JBI identifier of the artifact to stop.
| Auto-completion is available on artifacts IDs and artifact file names. |
If the artifact to deploy is a component or a service assembly, the command 'stop-artifact' will succeed only if the artifact state on Petals ESB side is 'STARTED', otherwise on error will occur.
Undeploying and Stopping an Artifact at once
Petals CLI is able to stop and uninstall/undeploy a JBI artifact without distinction between shared-library, component and service assembly using the following command:
undeploy [ -u <artifact-file> | -a <artifact-id> [<artifact-type>] ]
where:
- <artifact-file> is the local file name or the URL of the artifact to undeploy.
- <artifact-type> is the nature (SL, component, SA) of the artifact to undeploy.
- <artifact-id> is the JBI identifier of the artifact to undeploy.
| Auto-completion is available on artifacts IDs and artifact file names. |
No lifecycle error can occur. Whatever the artifact state, the command 'undeploy' will adapt to it to realize the undeployment. In particular, if the artifact is in state 'STOPPED', it will be undeployed without confirmation and the user will be responsible to re-deploy it.
Bulk Undeployment and Stop
The undeployment command is able to stop and uninstall/undeploy several JBI artifact in one shoot using the bulk mode:
undeploy [ -b [<artifact-directory>] ] [ -y ]
where [<artifact-directory> is a local directory name or the URL containing archives of artifacts to undeploy.
A confirmation is expected, except if the 'yes' flag is set on the command line or as command argument, otherwise an error will occur.
A confirmation message is displayed in the console mode, except if the 'yes' flag is set on the command line or as command argument.
> ./petals-cli.sh -y -c -- undeploy -b > ./petals-cli.sh -c -- undeploy -b -y > ./petals-cli.sh -c -- undeploy -b ERROR on command 'undeploy': A confirmation is required. Use option: : '-y'
If the directory, containing artifacts to undeploy, contains an artifact that is not deployed, a warning is displayed, no error occurs and the undeployment of other artifacts continues.
If an error occurs during the undeployment of an artifact, the bulk undeployment is interrupted.
Showing installed JBI artifacts
All the installed JBI artefacts can be listed using the command 'list [-p <artifact-pattern> ] [-t artifact-type]':
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- list petals-sl-mysql Installed SL petals-bc-soap Loaded BC petals-se-bpel Started SE soap-consume-provide Started SA su-SOAP-EchoService-consume SU su-SOAP-EchoService-provide SU
where:
- <artifact-pattern> is an optional RegExp pattern to filter the content of the returned list. All the returned JBI artifacts must have a JBI identifier matching the pattern. If no pattern is defined, all the installed artifacts are returned.
- <artifact-type> is one of the following values: SL, BC, SE, SA, SU, used to restrict the returned list.
The returned list is ordered:
- firstly, according to the artifact type: SL, BC, SE, SA, SU,
- and secondly the alphabetical order is applied.
For each artifact, the command displays (caution to the padding):
- Its JBI identifier.
- Its current status:
- Loaded, available only for component, the installer is loaded but the component is not installed
- Started
- Stopped
- Its type (SL, BC, SE, SA, SU).
| As the SU lifecycke can't be modified through the JMX API, there is no interest to display the SU status (it's the same as the status of its SA). |
Getting information about an Artifact
Information about a JBI artifact can be got with the 'show' command:
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- show [-e] [ -u <artifact-file> | -a <artifact-id> [<artifact-type>] ]
where:
- <artifact-file> is the local file name or the URL of the artifact to show.
- <artifact-type> is the nature (SL, component, SA) of the artifact to show.
- <artifact-id> is the JBI identifier of the artifact to show.
The '-e' option displays extended information.
Displayed information includes:
- For a shared library:
- Its JBI identifier
- The version of the shared library if available, extracted from its JBI descriptor
- If the shared library was built with Maven, its Maven version extracted from Maven metadata
- Extended information:
- List of embedded libraries (coming next)
- For a component (BC or SE):
- Its JBI identifier
- Its type: binding component or service engine
- If the component was built with Maven, its Maven version extracted from Maven metadata
- Its state (not-loaded, loaded, installed, started, stopped, shutdown)
- Extended information:
- List of embedded libraries of the boostrap classpath(coming next)
- List of embedded libraries of the runtime classpath(coming next)
- List of needed shared-libraries, for each shared-library(coming next):
- Its JBI identifier
- The version of the shared library if available, extracted from its JBI descriptor
- For a service assembly:
- Its JBI identifier
- If the service-assembly was built with Maven, its Maven version extracted from Maven metadata
- Its state (not-deployed, deployed, started, stopped, shutdown)
- List of embedded service-units (displayed using their JBI identifiers)
- Extended information (replace the previous list of embedded service-units):
- For each service unit embedded:
- Its JBI identifier
- Its target component (displayed using its JBI identifier)
| Auto-completion is available on artifacts IDs and artifact file names. |
Interrupting a flow of commands
A flow of commands can be interrupted by using the 'exit' command. If a number is set as argument, it is used as return code. The argument 'lastErrorCode' is used as return code value of the last executed command. Otherwise, 0 is returned to the shell.
> ./petals-cli.sh -y - << EOF deploy /tmp/my-artifact.zip exit lastErrorCode EOF
Ending a flow of commands
When the end of a flow of commands is reached, if the last command is not 'exit', the 'exit lastErrorCode' command is implicitly executed.
> ./petals-cli.sh -y - << EOF deploy /tmp/my-artifact.zip EOF echo $? 0
Working with the Container
Getting the versions related to a Petals node
To get the version of a Petals node, the version of the JVM running Petals node, and its operating system, use the 'version' command:
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- version Petals JBI Container 3.1.4-SNAPSHOT Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 1.6.0_26-b03 Linux 3.0.0-16-generic-pae
Stopping the container
The container can be stopped by using the command 'stop':
> ./petals-cli.sh -c -- stop
Shutdowning the container
The container can be shutdowned by using the command 'stop' and the parameter '--shutdown'.
> ./petals-cli.sh -C petals-cli@host:port> stop --shutdown Are you sure you want to shutdown the container? (y/n)
A confirmation is expected, except if the 'yes' flag is set on the command line or as command argument, otherwise an error will occur.
A confirmation message is displayed in the console mode, except if the 'yes' flag is set on the command line or as command argument.
> ./petals-cli.sh -y -c -- stop --shutdown > ./petals-cli.sh -c -- stop --shutdown -y > ./petals-cli.sh -c -- stop --shutdown ERROR on command 'stop': A confirmation is required. Use option: : '-y'
Getting the topology
When connected to a container, it is possible to get information about the topology of this node is part of.
petals-cli@host:port> topology-list Domain: Domain 1 Subdomain: SubDomain 1 * Container: Node1 ** information * Container: Node2 ** information Subdomain: SubDomain 2 ...
Sensible information as credentials are returned only if a security passphrase is provided. This passphrase can be provided using the command option '-p'. Otherwise, it is retrieve from the preferences file through the sub-property of alias: <alias>.passphrase.
petals-cli@host:port> topology-list -p mypassphrase Domain: Domain 1 Subdomain: SubDomain 1 * Container: Node1 ** information including credentials
This command shows a set of Petals nodes, sorted by domain and sub-domains, each node having the following information:
- Container name
- Node type (master or slave)
- Host
- Node ports
- Node credentials (only if the security passphrase is provided and correct)
Getting the server properties
When connected to a container, it is possible to get all the values defined in its server.properties file.
petals-cli@host:port> properties-list Key1: value1 Key2: value2 ...
where "keyN" and "valueN" are the keys and values defined in the server.properties file of this container.
Changing logger levels
On a container, it is possible to change the level of a logger.
petals-cli@host:port> logger-set -n <logger-name> -l <level> The log level was succesfully changed.
In case of error, the error message is "The log level could not be changed.", followed by a detailed message (e.g. "WARN is not a valid log level").
To get all the available loggers with their level, use the command loggers without any argument.
petals-cli@host:port> loggers <logger-name-1> <level> <logger-name-2> <level> ...
You can also use a regular expression to filter the candidate results.
petals-cli@host:port> loggers -p <regular expression> <logger-name-1> <level> <logger-name-2> <level> ...
| Auto-completion is available on logger names and log levels. |
Working with the Service Registry
| Qualified names, like service and interface names, are written as follows:{namespace-uri}local-part. |
Synchronizing the registry
A synchronization of the registry on a specific node can be done with the 'registry-sync' command:
> registry-sync Synchronization is done
A synchronization of all the topology nodes can be done with the same command and the '-a' argument.
> registry-sync -a <Progress Report (as a percentage)> Synchronization is done
Global synchronization is done in two passes:
|
The response message is displayed in console mode only.
Showing the registry's full content
The full content of the registry can be dumped by using the 'registry-list' command:
petals-cli> registry-list Endpoints: <endpoint-name-1>: <endpoint-1-characteristics> <endpoint-name-2>: <endpoint-2-characteristics> Services: <service-name-1>: <endpoints-list> <service-name-2>: <endpoints-list> Interfaces: <interface-name-1>: <endpoints-list> <interface-name-2>: <endpoints-list>
where:
- <endpoint-name-x> is an endpoint name.
- <endpoint-x-characteristics> is the attributes of the endpoint, separated by comma: container identifier, component identifier, endpoint type.
- <service-name-x> is a service name.
- <interface-name-x> is an interface name.
- <endpoints-list> is the list of endpoint name implementing the interface or service.
Filtering the registry's full content
The content of the registry can be dumped by using the 'registry-list' command.
It is however possible to filter the dumped result.
petals-cli> registry-list \[-e <endpoint-name-regexp>\] \[-s <service-name-regexp>\] \[-i <interface-name-regexp>\] Endpoints: <endpoint-name>: <endpoint-characteristics> Services: <service-name-1>: <endpoint-name> <service-name-2>: <endpoint-name> Interfaces: <interface-name-1>: <endpoint-name> <interface-name-2>: <endpoint-name>
where:
- <endpoint-name-regexp> is a regular expression used as filter on the full end-point name.
- <service-name-regexp> is a regular expression used as filter on the full service name.
- <interface-name-regexp> is a regular expression used as filter on the full interface name.
In the result:
- <endpoint-name> is the endpoint name.
- <endpoint-characteristics> is the attributes of the endpoint, separated by comma: container identifier, component identifier, endpoint type.
- <service-name-x> is the services associated to the specified endpoint.
- <interface-name-x> is the interface names associated with the specified endpoint.
The parameter order (endpoint, service, interface) does not matter.
All are optional. If none is specified, the entire regitry content is dumped.
System Commands
Petals CLI can directly execute system commands.
To achieve it, the system command is an argument of the 'system' command.
petals-cli> system <system-command>
As an example,
petals-cli> system pwd
displays the directory in which Petals CLI runs.
The return code of the wrapping command is the return code of the system command.
To execute a system command having arguments, you MUST enclosed it with quotes:
petals-cli> system "echo linux"
|
Caution to correctly escape the symbol '$' when using a system command with variable on command line:
$ petals-cli -c -- system echo My linux temporary folder: \${java.io.tmpdir}
My linux temporary folder: /tmp
$ petals-cli -c -- system "echo My linux temporary folder: \${java.io.tmpdir}"
My linux temporary folder: /tmp
|
Advanced usage
Logging in Petals CLI
Petals CLI is provided with a default Java Logging configuration. This configuration displays logging trace as following:
<LEVEL>: <message>
where <LEVEL> is the international label of the logging trace level, except for the level 'SEVERE' which is always 'ERROR'. By default, only levels 'SEVERE' and 'WARNING' are printed.
The default configuration can be overridden using the system property 'java.util.logging.config.file' to set into the launching script '$PETALS_CLI_HOME/bin/petals-cli.sh' or '%PETALS_CLI_HOME%\bin\petals-cli.bat'. An sample configuration is available in file '$PETALS_CLI_HOME/conf/petals-cli-logging-sample.properties'
To add your custom command
Petals CLI is provided with an API to add your own command.
Writing your command
To create a new custom command, just create a new Java class that IMPLEMENTS the interface org.ow2.petals.cli.api.command.Command.
To be auto-discovered, your command MUST be declared in a resource named 'META-INF/service/org.ow2.petals.cli.api.command.Command' (put the class name with the package part in this file).
If the new command needs third party products in addition of the ones already provided by Petals CLI, they MUST be installed with your command.
| No classloader isolation is available between commands, pay attention to versions of third-party products. They MUST match the version of those provided with Petals CLI or those custom commands. |
Custom command installation
To install your command just put all needed JAR files in the directory $PETALS_CLI_HOME/extensions.
Monitoring Petals with Petals CLI
An extension of Petals CLI was created to monitor Petals ESB.
This extension has several implementations. Each implementation is adapted to a monitoring tool, but can be used as a normal command. Now, only one implementation exist, the Cacti's implementation
Known Problems
Error about missing options
For commands requiring at least one option, an error can occur if the operand flag ('--') is missing:
> ./petals-cli.sh -h localhost -n 7700 -u petals -p petals -c -- deploy -u file:///.../my-archive.zip
ERROR on command 'deploy': Missing option(s):b, u
usage: deploy [-b <url> | -u <url>] [-D
<property1=value1,property2=value2> | -f <configuration-file>]
This is due to the option overriding: the command deploy and Petals CLI have the same option: -u. Both -u are processed by Petals CLI option parsing. Just add '--' before the command to exclude the second 'u' of the Petals CLI option parsing. So it will be available for the command option parsing.
Can not connect using URI : service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://<host>:7700/jmxRmiConnector with petals/petals
This error can reveal several configuration problems:
- a mistake in the Petals ESB container configuration at topology level:
If you are running Petals ESB with its default configuration on a host 'A', you will get the following error connecting the Petals CLI from another host 'B':ERROR: org.ow2.petals.jmx.api.api.exception.ConnectionErrorException: Can not connect using URI : service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://192.168.0.11:7700/jmxRmiConnector with petals/petalsBy default, Petals ESB listens JMX connection from localhost, that's why you get the error. Update the host name of the Petals ESB in its topology configuration file to solve the problem.
- a mistake in your network configuration at system level:
On Linux system, check your file /etc/hosts. If declared, the host running the Petals ESB container must be correctly defined with its IP address.
Petals CLI seems to be frozen on command 'exit'
You entered the command exit in the interactive mode, and the Petals CLI seems to be frozen: no prompt.
You probably have launched asynchronous commands as defect subscriptions, use Ctrl-C to force to exit the Petals CLI or kill its process.