SummaryThis tutorial explains how you can make expose a JMS queue or a JMS topic as a service in Petals ESB.
|
Creating the Service-Unit project
Getting started
Start Petals Studio.
In the menu, select File > New > Service-Unit Project.
If you do not see it, go into File > New > Other... Then, select Service-Unit Project under the Petals category.
A wizard opens up, showing three drop-down lists.
In the Use Case list, select Provide or Import a Service into Petals.
In the Petals Component list, select JMS // petals-bc-jms.
In the Component Version list, select the version of the Petals-BC-JMS that you are using in Petals.
In the scope of this tutorial, we are going to work with the version 3.1 of the JMS component.
Which gives us:
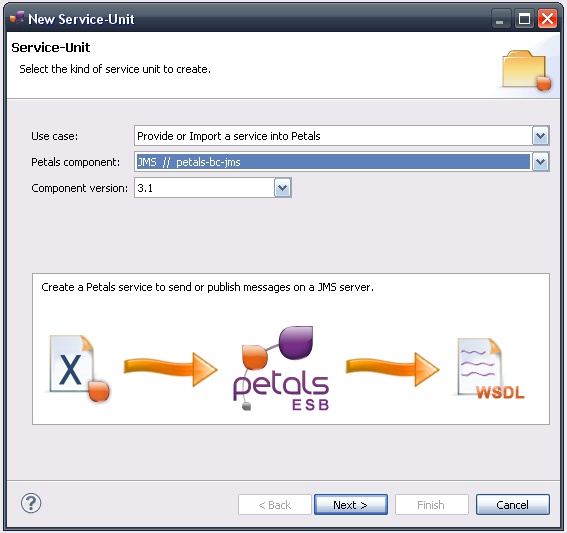
Click Next.
Identifying the service
The current page requires you to fill-in the base information to put in the JBI descriptor (META-INF/jbi.xml).
In particular, it defines the interface, service and end-point names of the service that is imported.
If you have a WSDL to describe this service, these fields can be filled-in automatically from this WSDL file.
Otherwise, you have to complete the interface, service and end-point names by hand.
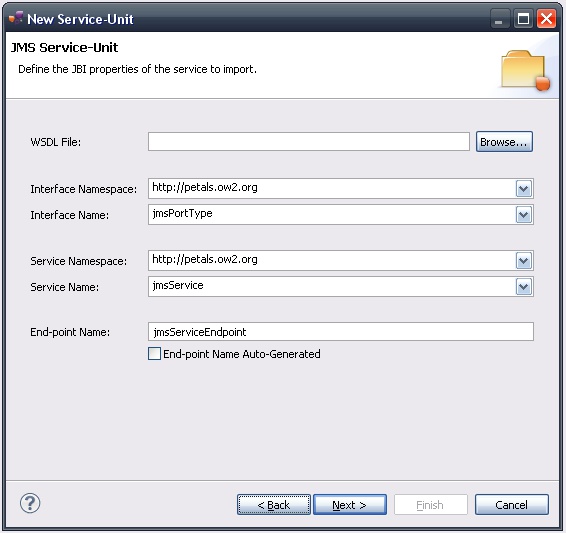
| There is no default WSDL for this component. |
If the WSDL definition is accessible through an URL, then copy its URL in the WSDL file field.
If the WSDL definition of the Web Service is located on the local disk, click Browse... and select your WSDL on the disk.
| The auto-generation of the end-point (visible as a check box on the screen-shot) should not be used with the JMS component. |
Once the WSDL location and the fields have been filled-in, click Next.
Defining the project name
This page defines the name and the location of the project that will be created.
Indeed, this wizard will result in the creation of a project containing all the required elements for a JMS service-unit.
Enter a project name for your project.
If you do not want your project to be created in the default workspace, uncheck Use default location.
Then click Browse... and select the location where the project will be created.
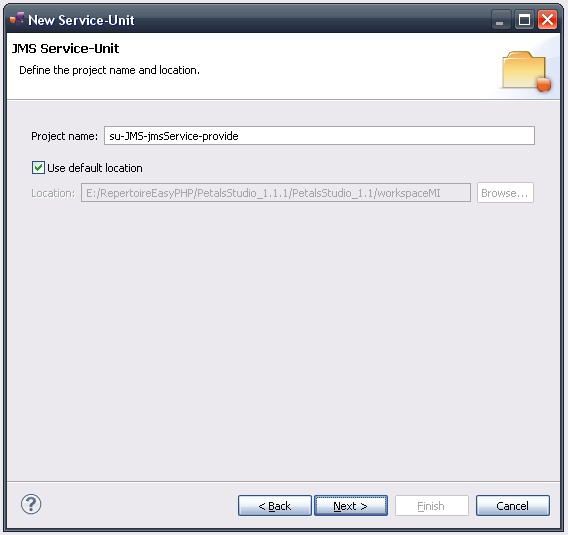
| Petals service-units have a naming convention. For a service-unit which provides a service, the convention is su-<Protocol or Technology>-<Service name>-provide |
Then, click Next.
Specifying the JMS parameters
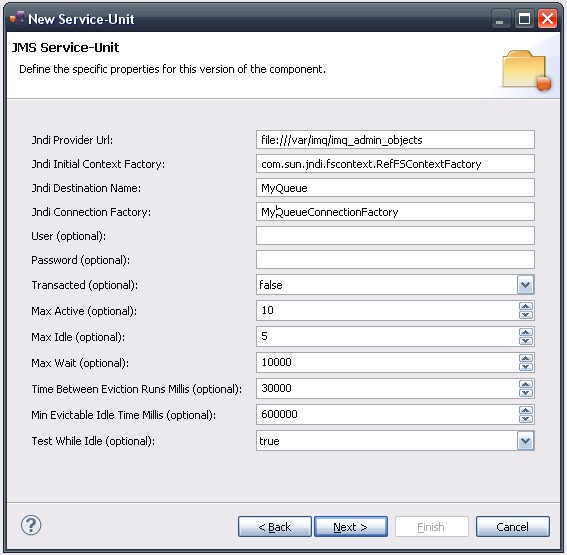
This page defines information which are specific to the Petals JMS component.
The required parameters are all about the JNDI properties and the JNDI-configuration of the JMS server.
The meaning of all the parameters can be read in the documentation of the Petals-BC-JMS component.
Click Next.
Specifying the CDK parameters
The CDK is the Petals framework to develop JBI components.
The Petals-BC-JMS component was developed with this framework.
This page requires information related to the CDK.
By default, you have nothing to do here.
The meaning of all the CDK parameters for JMS can be found in the documentation of the Petals-BC-JMS component.
Click Finish to complete the wizard.
Checking the result
When the wizard has completed, a new project has been created and is visible in your workspace.
It contains a jbi.xml file, located under src/main/jbi.
This hierarchy allows you to work with Apache Maven then (a pom.xml was also created at the root of the project).
In the same directory, and if you provided a WSDL in the wizard, you can see your WSDL interface, which was imported with all its dependencies (e.g. referenced XML schemas or other WSDL interfaces).

Updating, packaging and deploying
Further edition and packaging
After completion, the newly created jbi.xml file has been open in the Service-Unit editor.
Regarding JMS configurations, the wizards are complete and provide all the options.
Thus, you do not need to edit the jbi.xml.
The project contains everything the JMS component needs.
You can now package it before deploying it.
The created project being a Service-Unit project, you can package it as any Service-Unit project.
It results in the creation of a Service Assembly for the Petals-BC-JMS component. Its location depends on your export choices.
Deployment
The deployment of the created service assembly can be achieved with the Petals web console.
Or you can do it by dropping the service assembly in the install directory of your Petals installation.
This second option should only be used in development steps.
First, make sure the Petals-BC-JMS is installed in your Petals environment.
Then, install the service assembly in your Petals, using one of the two ways indicated above.
Be careful, the Petals JMS component cannot be used as it.
It needs to be configured to use the shared-library associated with your JMS server.
You may also have to create this shared-library, in case where your JMS server is not supported by the Petals team.
Do not worry, creating a shared-library is very easy with the Petals Maven plug-in (provided you are familiar with Maven).
And configuring the JMS (or any other Petals) component to use a shared-library can be achieved with the Petals Maven plug-in.