Installation
Nagios installation
The Nagios integration was experienced on a Linux distribution "Ubuntu Maverick Meerkat (10.10)".
Nagios 3 is available through the default Ubuntu repository. So, just install the package "nagios3" using the standard way.
Enabling the SNMP agents of the Petals ESB JVMs
As the monitoring tools can use SNMP probes to get information from the JVM running Petals ESB, we need to enable the SNMP agent of the JVM of each Petals ESB node.
Waiting a better manner to enable the SNMP agent, on each Petals node, add the following system properties on the java command line of the script starting Petals ESB:
-Dcom.sun.management.snmp.port=16161 -Dcom.sun.management.snmp.acl.file=$PETALS_HOME/conf/snmp.acl
where:
- com.sun.management.snmp.port defines the listen port of the SNMP agent.
 | Caution, if Petals ESB runs with a user different from root, you need to use a port upper than 1024. To use a port lower than 1024 with a Petals ESB launches with a standard user, refers to the utility privbind (available in standard Ubuntu repository). |
 | To use the same port on the same machine for several java processes, refers to snmpd used as proxy. |
- com.sun.management.snmp.acl defines the path file defining ACL of the SNMP agent. It is recommended to create a specific file from $JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/management/snmp.acl where you can configure for example the following ACL entry:
acl = {
{
communities = public, private
access = read-only
managers = localhost
}
}
 | Caution, this file should be accessible only by the user running the JVM process. |
Nagios configuration
JVM host template
A best practice to monitor Java application is to create a template 'JVM host'.
According to our environment defined above, create the file 'jvm-host-nagios2.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
define host{
use generic-host
name jvm-host ; The name of this host template
notifications_enabled 1 ; Host notifications are enabled
event_handler_enabled 1 ; Host event handler is enabled
flap_detection_enabled 1 ; Flap detection is enabled
failure_prediction_enabled 1 ; Failure prediction is enabled
process_perf_data 1 ; Process performance data
retain_status_information 1 ; Retain status information across program restarts
retain_nonstatus_information 1 ; Retain non-status information across program restarts
check_command check-host-alive
max_check_attempts 10
notification_interval 0
notification_period 24x7
notification_options d,u,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS DEFINITION - ITS NOT A REAL HOST, JUST A TEMPLATE!
# Specific attributes
_snmp_port 161 ; Listening port of the JVM SNMP agent
}
Nagios commands definition to interact with a SNMP agent
We recommand to define specific Nagios command to interact with the Java virtual machine MIB.
Interresting commands will be:
- jvm_heapused: to get the real heap memory used by the Petals ESB node,
- jvm_heapmaxused: to get the current allocated (commited) heap size. This value should be check against the heap max size at the JVM level to generate alarms.
According to our environment defined above, create the file 'jvm.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios-plugins/config' with the following content:
# 'jvm_heapused' command definition
define command{
command_name jvm_heapused
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_snmp -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -p '$_HOSTSNMPPORT$' -C '$ARG1$' -P '$ARG2$' -o 1.3.6.1.4.1.42.2.145.3.163.1.1.2.11.0 -w :'$ARG3$' -c :'$ARG4$' -l load
}
# 'jvm_heapmaxused' command definition
define command{
command_name jvm_heapmaxused
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_snmp -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -p '$_HOSTSNMPPORT$' -C '$ARG1$' -P '$ARG2$' -o 1.3.6.1.4.1.42.2.145.3.163.1.1.2.12.0 -w :'$ARG3$' -c :'$ARG4$' -l load
}
Petals ESB host template
A best practice to monitor Petals ESB nodes is to create a template 'Petals ESB host' that inherites from the 'JVM host'.
According to our environment defined above, create the file 'petals-esb-host-nagios2.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
define host{
use jvm-host
name petals-esb-host ; The name of this host template
notifications_enabled 1 ; Host notifications are enabled
event_handler_enabled 1 ; Host event handler is enabled
flap_detection_enabled 1 ; Flap detection is enabled
failure_prediction_enabled 1 ; Failure prediction is enabled
process_perf_data 1 ; Process performance data
retain_status_information 1 ; Retain status information across program restarts
retain_nonstatus_information 1 ; Retain non-status information across program restarts
check_command check-host-alive
max_check_attempts 10
notification_interval 0
notification_period 24x7
notification_options d,u,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS DEFINITION - ITS NOT A REAL HOST, JUST A TEMPLATE!
# Specific attributes
_snmpport 161 ; Listening port of the JVM SNMP agent
}
Defining your Petals ESB hosts
For each Petals ESB node of your Petals ESB topology, create an instance of the template 'petals-esb-host'.
According to our environment defined above, create the file 'petals-esb-host-node1.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
define host{
use petals-esb-host ; Name of host template to use
host_name petals-esb-node-1
alias Petals ESB Node 1
address 127.0.0.1
_snmpport 16161 ; This value should be set with the SNMP
; agent listener port of your Petals ESB node.
}
and create the file 'petals-esb-host-node2.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
define host{
use petals-esb-host ; Name of host template to use
host_name petals-esb-node-2
alias Petals ESB Node 2
address 127.0.0.1
_snmpport 16162 ; This value should be set with the SNMP
; agent listener port of your Petals ESB node.
}
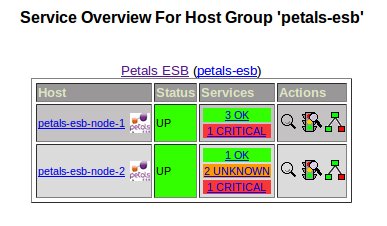
Defining your Petals ESB topology as a Petals ESB host group
The Petals ESB topology can be considered as a Nagios host group composed of your Petals ESB nodes.
So, according to our environment defined above, create the file 'petals-esb-hostgroup.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
define hostgroup {
hostgroup_name petals-esb
alias Petals ESB
members petals-esb-node-1, petals-esb-node-2
}
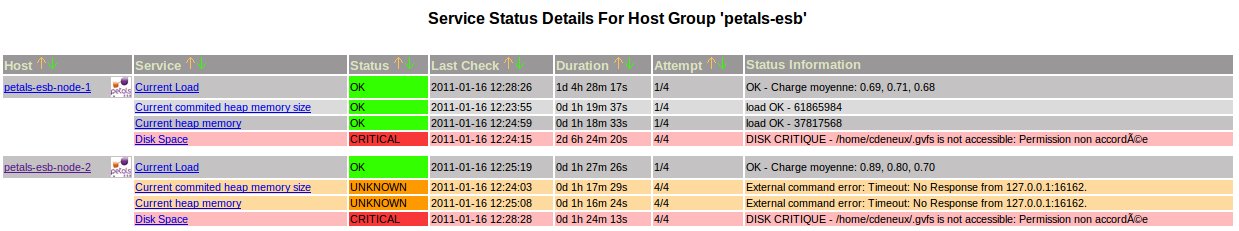
Petals ESB host services
A best practice to monitor Petals ESB nodes is to create a template of services to associate to each Petals ESB nodes.
According to our environement defined above, create the file 'petals-esb-services.cfg' in the directory '/etc/nagios3/conf.d' with the following content:
# Define a service to check the disk space of the root partition# Define a service to check the disk space of the root partition
# on the local machine. Warning if < 20% free, critical if
# < 10% free space on partition.
define service{
use generic-service
hostgroup_name petals-esb
service_description Disk Space
check_command check_all_disks!20%!10%
}
# Define a service to check the load on the local machine.
define service{
use generic-service
hostgroup_name petals-esb
service_description Current Load
check_command check_load!5.0!4.0!3.0!10.0!6.0!4.0
}
# Define a service to check the heap memory used by Petals ESB node.
# Warning if > 85% configured max heap size, critical if 95% configured
# max heap size.
# Note: The value returned by the SNMP Get is a byte value. So, for
# a max heap size of 1Go:
# 85% => 912680550 bytes,
# and 95% => 1020054733 bytes
define service{
use generic-service
hostgroup_name petals-esb
service_description Current heap memory
check_command jvm_heapused!public!2c!912680550!1020054732
}
# Define a service to check the max (commited) heap memory used by Petals ESB node.
# Warning if > Warning if > 85% configured max heap size, critical if 95% configured
# max heap size.
# Note: The value returned by the SNMP Get is a byte value. So, for
# a max heap size of 1Go:
# 85% => 912680550 bytes,
# and 95% => 1020054733 bytes
define service{
use generic-service
hostgroup_name petals-esb
service_description Current commited heap memory size
check_command jvm_heapmaxused!public!2c!912680550!1020054732
}
Restart Nagios
Restart your Nagios service to take into account the configuration. |