Introduction
|
Several concurrent life-cycles exist in Petals ESB: |
Table of contents Contributors
No contributors found for: authors on selected page(s)
|
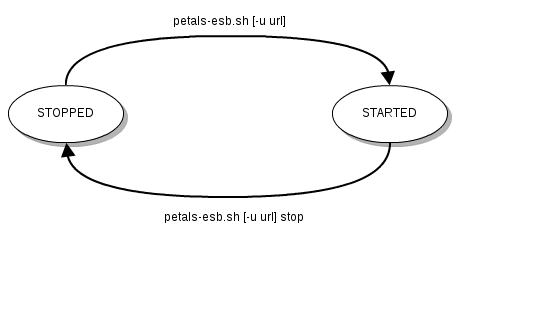
The Petals ESB life-cyle
The Petals ESB life-cycle is very simple.
|
It contains only one state: STARTED. The implicit state 'STOPPED' does not really exist because in such state no Petals ESB process is running.
The transition from state 'STOPPED' to 'STARTED' is realized using the Petals ESB startup script 'petals-esb'. The return to the state 'STOPPED' is realized using ^C or the command 'petals-esb stop'. See Starting and stopping Petals ESB.
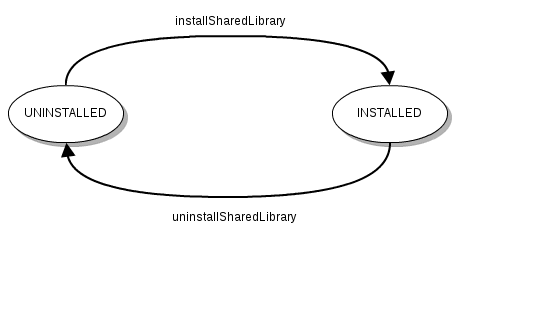
The shared-library life-cyle
The life-cycle
The shared-library life-cycle is simple.
|
It contains only one state: INSTALLED. The implicit state 'UNINSTALLED' does not really exist because the shared-library is not instantiated or loaded.
The transition from state 'UNINSTALLED' to 'INSTALLED' is realized installing the shared library, and the return to the state 'UNINSTALLED' is realized uninstalling the shared-library. A shared library can be (un)installed using Petals CLI, the Petals Autoloader, Petals Ant Tasks or the JMX API.
Constraints
The shared library life-cycle is linked to the component life-cycle:
- a shared library required by a component must be installed before to load the component
- a shared library can not be uninstalled until a component requiring it is installed.
| Component state | installSharedLibrary | uninstallSharedLibrary |
|---|---|---|
| UNLOADED |  |
 |
| LOADED/UNINSTALLED |  |
 |
| INSTALLED/SHUTDOWN |  |
 |
| STOPPED |  |
 |
| STARTED |  |
 |
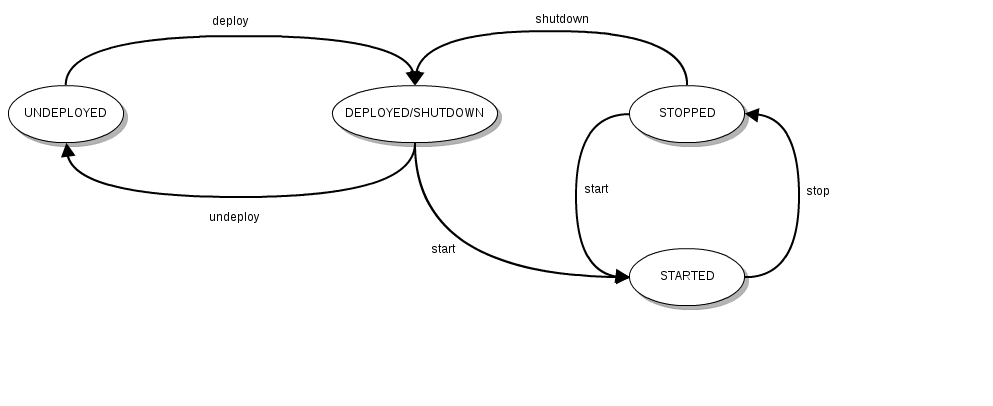
The component life-cycle
The life-cycle
The component life-cycle is the more complex life-cycle of Petals ESB life-cycles. It is composed of two correlated sub life-cycles:
- the component installer life-cycle that drives the installation of the component,
- the component life-cycle itself.
|
Constraints
The component life-cycle is linked to:
- the shared life-cycle,
- the service-unit lifecycle.
- and have following constraint against the service-unit life-cyle:
Service unit state loadNewInstaller install start stop shutdown uninstall unloadInstaller UNDEPLOYED 






SHUTDOWN 






STOPPED 






STARTED 






- component required by a service unit must be installed and running (ie. in state STOPPED or STARTED) before to deploy the service unit,
- if service units are deployed on, a component can only be started or stopped. All service units must be undeployed before to try any other transitions.
The service-assembly life-cycle
The service assembly life-cycle can be viewed as a wrapper of its all service unit life-cycles. It propose to drive the life-cycle of its service-units in on operation.
|
The transitions from state 'UNDEPLOYED' to 'SHUTDOWN' is realized deploying the service assembly, and the return to the state 'UNDEPLOYED' is realized undeploying the service assembly. A service assembly can be (un)deployed/started/stopped/shutdown using Petals CLI, the Petals Autoloader, Petals Ant Tasks or the JMX API.
The service-unit life-cyle
The service unit life-cycle is simple:
|
The implicit state 'UNDEPLOYED' does not really exist because the service unit is not deployed.