SummaryThis tutorial explains how you can invoke a Petals service when a file is added in a directory.
|
Creating the Service-Unit project
Getting started
Start Petals Studio.
In the menu, select File > New > Service-Unit Project.
If you do not see it, go into File > New > Other... Then, select Service-Unit Project under the Petals category.
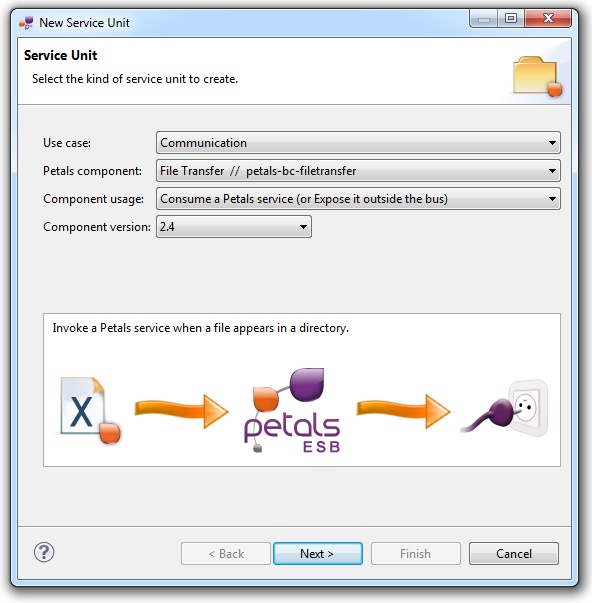
A wizard opens up, showing three drop-down lists.
In the Use Case list, select Communication.
In the Petals Component list, select File Transfer // petals-bc-filetransfer.
In the Component Usage list, select Consume a Petals service (or Expose it outside the bus).
In the Component Version list, select the version of the Petals-BC-FileTransfer that you are using in Petals.
In the scope of this tutorial, we are going to work with the version 2.4 of the File Transfer component.
Which gives us:
Click Next.
Identifying the target service
The current page requires you to fill-in the base information to put in the JBI descriptor (META-INF/jbi.xml).
In particular, it defines the interface, service and end-point names of the service that will be invoked when a file is added in the watched directory.
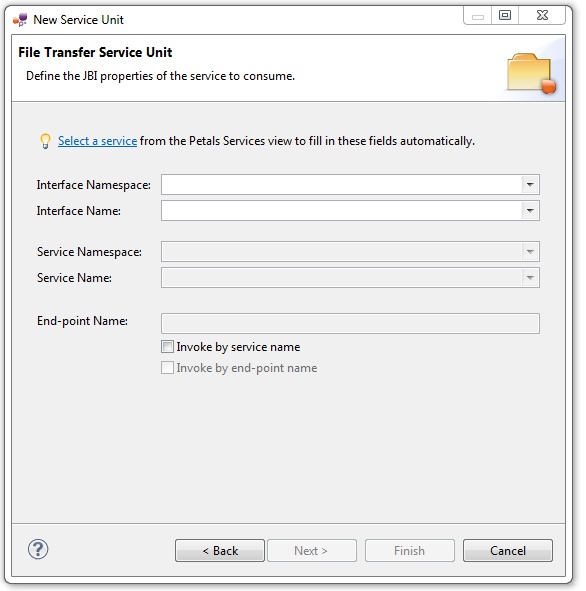
| A service is identified by a triplet, interface, service and end-point names. This triplet is unique in a Petals topology. When you consume a service, the service is selected in a set. This set is defined by the invocation properties. If the 3 fields are set in the consume properties, then the set will contain at most 1 result (there can be only 1 service with this ID). Consume possibilities are the following ones:
|
You can obviously fill-in these fields by hand.
However, the most efficient way is to use the Petals Services explorer (provided it was populated).
Click Select a service. A selection dialog shows up, providing filtering assistance.
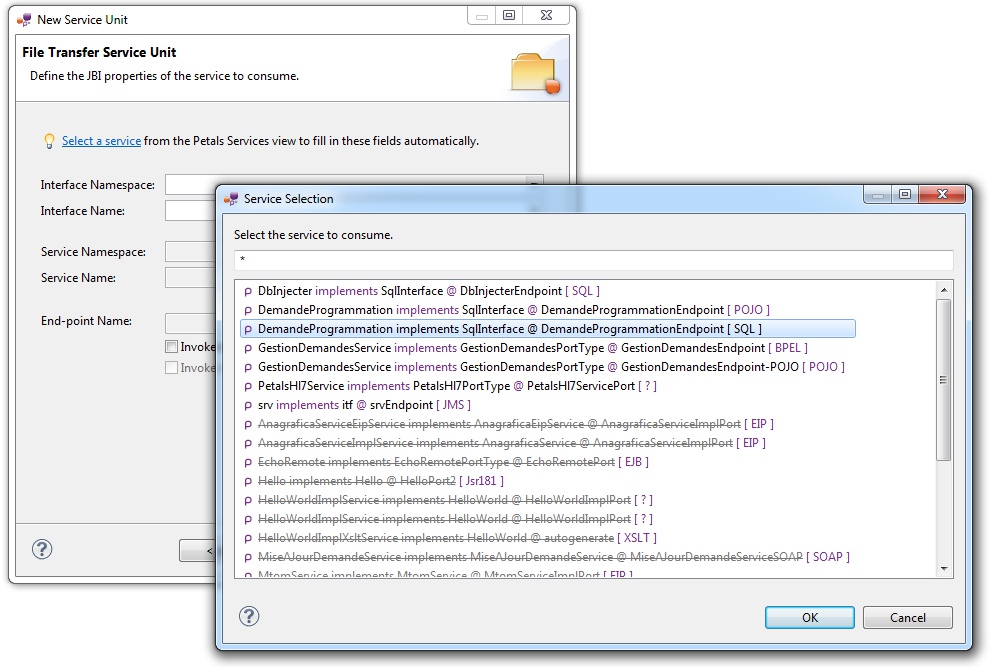
When you have selected your service, click OK.
The wizard fields are filled-in automatically.
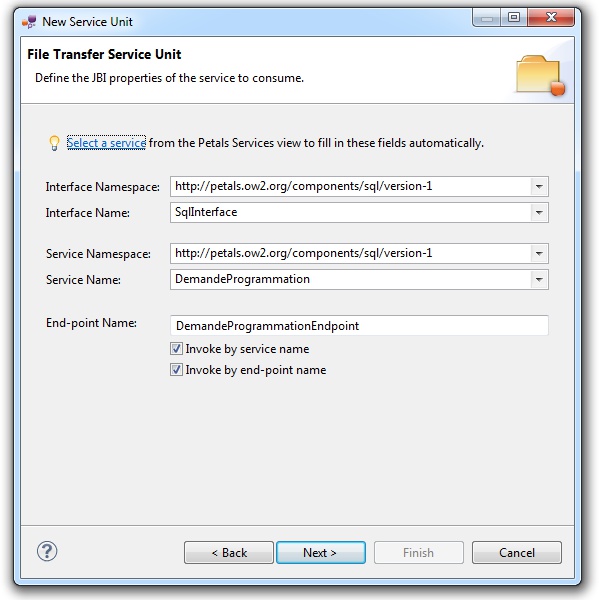
| The values for the interface, service and end-point names must match the values defined in the jbi.xml of the invoked service. Indeed, this service must be a Petals service, and thus be described in a jbi.xml. As a reminder, the jbi.xml values and the WSDL values (if the WSDL exists) of the invoked service must be exactly the same. For this reason, filling-in the information by hand or modifying it is discouraged. |
Click Next.
Defining the project name
This page defines the name and the location of the project that will be created.
Indeed, this wizard will result in the creation of a project containing all the required elements for a File Transfer service-unit.
Enter a project name for your project.
If you do not want your project to be created in the default workspace, uncheck Use default location.
Then click Browse... and select the location where the project will be created.
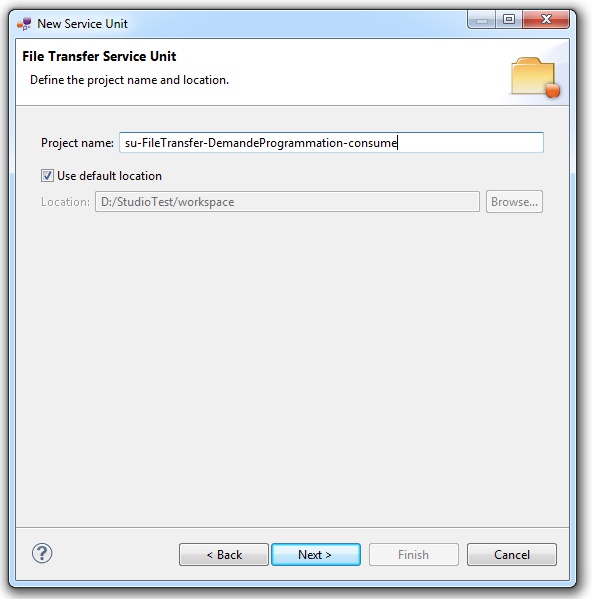
| Petals service-units have a naming convention. For a service-unit which consumes (calls) a service, the convention is su-<Protocol or Technology>-<Service name>-consume |
Then, click Next.
Specifying the File Transfer parameters
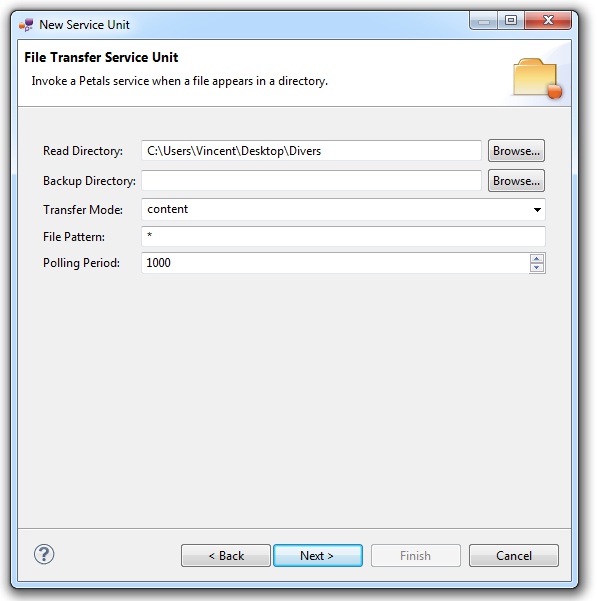
This page defines information which are specific to the Petals File Transfer component.
There are three parameters to take care of here:
- There is the directory that will be polled regularly.
- There is the name pattern of the file that must be sent to the invoked service.
- And there is the polling period, i.e. the time interval between each polling of the read directory.
The other displayed parameters are optional.
The meaning of all the parameters can be read in the documentation of the Petals-BC-FileTransfer component.
Click Next.
Specifying the CDK parameters
The CDK is the Petals framework to develop JBI components.
The Petals-BC-FileTransfer component was developed with this framework.
This page requires information related to the CDK.
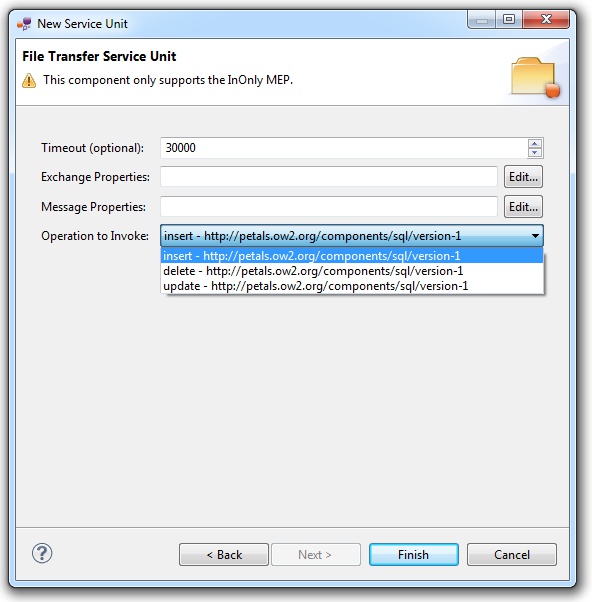
If the service to consume is described by a WSDL, then there is a list of the possible operations that can be invoked.
Otherwise, you have three parameters to complete here (others are optional or have default values):
- The name space of the invoked operation's name (WSDL operations are QNames).
- The local part of the invoked operation's name (WSDL operations are QNames).
- The Message Exchange Pattern (MEP).
With this component, only operations that work with the InOnly MEP can be invoked.
The wizard only shows these operations.
The meaning of all the CDK parameters for File Transfer can be found in the documentation of the Petals-BC-FileTransfer component.
Click Finish to complete the wizard.
Checking the result
When the wizard has completed, a new project has been created and is visible in your workspace.
It contains a jbi.xml file, located under src/main/jbi.
This hierarchy allows you to work with Apache Maven then (a pom.xml was also created at the root of the project).
There is nothing else in the project.

Updating, packaging and deploying
Further edition and packaging
After completion, the newly created jbi.xml file has been open in the Service-Unit editor.
Regarding File Transfer configurations, the wizards are complete.
The project contains everything the File Transfer component needs.
You can now package it before deploying it.
The created project being a Service-Unit project, you can package it as any Service-Unit project.
It results in the creation of a Service Assembly for the Petals-BC-FileTransfer component. Its location depends on your export choices.
Deployment
The deployment of the created service assembly can be achieved with the Petals web console.
Or you can do it by dropping the service assembly in the install directory of your Petals installation.
This second option should only be used in development steps.
First, make sure the Petals-BC-FileTransfer is installed in your Petals environment.
Then, install the service assembly in your Petals, using one of the two ways indicated above.
There is no need to update configuration of the File Transfer component to make it work.
Using the default settings is enough to make the service-unit work.