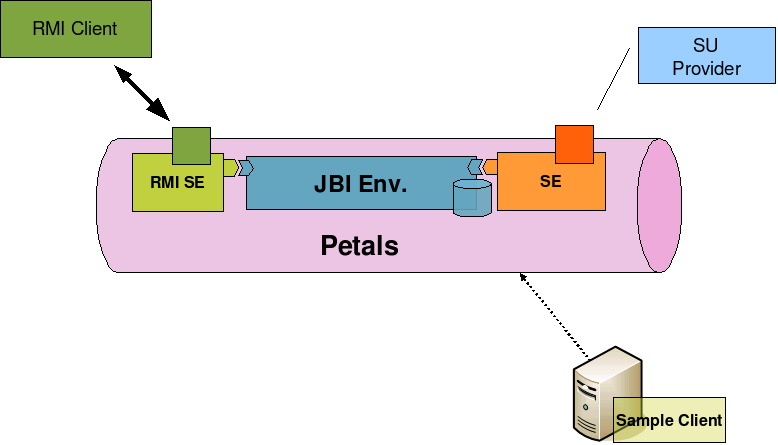
IntroductionFeaturesThe Petals RMI service engine aims to provide a direct access to the internal NMR of a Petals ESB container. So an external Java client can interact directly with the NMR:
Petals SE RMI overview
 Recommended usageThis component should be used in test context, for example for integration tests of JBI components.This component is distributed with the Petals Community Pack, and we discourage you from using it in a production environment. |
Table of contents
Contributors
No contributors found for: authors on selected page(s)
|
Usage
Once the RMI component is started, it binds a representation of its component context in the RMI registry. A client is thus able to access to this remote representation of the component context to create severals endpoints and communicate with others JBI services.
From this remote component context, the client can get the RMI representation of :
- the delivery channel,
- the message exchange factory.
The RMI client can also :
- receive JBI messages,
- send JBI messages.
To make easier these different actions, a client library is provided. The next section of this document defines how to use this library to create an RMI client.
| The current version of the Petals SE RMI registers only one remote component context. So, just one client can be connected to this context on this component. This restriction will be deleted in a next version of the component. For now, if you want install several clients, you must install several Petals SE RMI components. |
Implementing RMI client interacting with a Petals SE RMI
Your RMI client will depend on the following Maven artifacts as RMI client libraries:
- org.ow2.petals:petals-rmi-proxyclient,
- org.ow2.petals:petals-rmi-server:1.5.0,
- org.ow2.petals:petals-rmi-common:1.4.1
that embed classes mentioned below.
Accessing the RMI registry
The client package of the RMI component contains only one class (the ComponentContextLocator). To instantiate an object of this class, three inputs parameters are required in the constructor:
- the IP address of the RMI registry server,
- the port to access to the RMI registry (the port used by the RMI registry to handle requests),
- the reference name of the remote component context registered in the RMI registry.
The instantiation of object of this class is presented below:
ComponentContextLocator ccl = new ComponentContextLocator("192.168.1.150", 1099, "RMIComponentContext");
To avoid some errors, you must inserted this line code below at the beginning of the program
System.setProperty("com.sun.xml.namespace.QName.useCompatibleSerialVersionUID", "1.0"); |
| If the Petals SE RMI component is not started when the ComponentContextLocator object is instantiated, a remote exception is raised. |
Once the object is instantiated, it is possible to access to remote component context.
Getting the remote component context and activate/deactivate endpoints
The code lines presented below allows a client to access to the remote component context, to activate and deactivate an endpoint:
// Access to the remote component context from the ComponentContextLocator RemoteComponentContext rcc = ccl.getComponentContext(); // Activation of an endpoint ServiceEndpoint endpoint = rcc.activateEndpoint(new QName("http://petals.objectweb.org/", "RmiService"), "RmiEndpoint"); // Deactivation of the endpoint rcc.deactivateEndpoint(endpoint);
Getting the remote message exchange factory and create different kind of messages
The code lines presented below allows a client to access to the remote message exchange factory and create different kind of messages:
// Access to the remote message exchange factory from remote component context RemoteMessageExchangeFactory rmef = rcc.getDeliveryChannel().createExchangeFactory(); // create an in only message exchange MessageExchange msgInOnly = rmef.createInOnlyExchange(); // create an in out message exchange MessageExchange msgInOut = rmef.createInOutExchange(); // create an in optional out message exchange MessageExchange msgOptionalOut = rmef.createInOptionalOutExchange(); // create an robust in only message exchange MessageExchange msgRobustInOnly = rmef.createRobustInOnlyExchange();
Getting the remote delivery channel and send/accept JBI messages
The following code snippet allows a client to access to the remote delivery channel:
// Access to the remote delivery channel from remote component context RemoteDeliveryChannel rdc = rcc.getDeliveryChannel(); The following code snippet shows an asynchronous message exchange between the client and a provider: // Send a asynchronous message rdc.send(msgInOnly); // Accept the response of provider MessageExchange msgResponseInOnly = rdc.accept();
The following code snippet shows an synchronous message exchange between the client and a provider:
// Send a synchronous message msgInOut = rdc.sendSync(msgInOut); if(msgInOut != null) { // Change the status msgInOut.setStatus(ExchangeStatus.DONE); // Terminate the exchange rdc.send(msgInOut); }
| The method 'sendSync' is not JBI compliant. It is different of JBI interface because the message exchange in input parameter is not a remote object. So, it cannot be set in the method. |
Installation
The installation of the RMI component is achieved in the same way as classical components, please refer to the user guide for more details.
Configuration
This component is not based on the Petals CDK, so all standard configuration parameters are not available.
| Parameter | Description | Default | Required | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| port | The port used by the RMI component to contact the RMI registry. | 1099
|
No
|
Installation
|
| host | The hostname where the RMI registry is running. | -
|
No
|
Installation
|
| embeddedregistry | Defines if the internal RMI registry of the component must be activated. By default, the internal RMI registry is started on the port defined by the parameter 'port'. If this parameter is set to false, the administrator of the Petals SE RMI component is in charge to manage and start his own RMI registry before starting the RMI component. The hostname of the RMI registry must be set using the parameter 'host' | true
|
No
|
Installation
|
| componentcontextname | Define the reference name registered in the RMI registry when the bind with the remote component context is realized. This remote component context is just a representation of the concrete component context of PEtALS. No direct access to a concrete component is provided to clients. | RMIComponentContext
|
No
|
Installation
|
Definition of the parameter 'scope':
- Installation: The parameter can be set during the installation of the component, by using the installation MBean (see JBI specifications for details about the installation sequence). If the parameter is optional and has not been defined during the development of the component, it is not available at installation time.
- Runtime: The parameter can be set during the installation of the component and during runtime. The runtime configuration can be changed using the CDK custom MBean named RuntimeConfiguration. If the parameter is optional and has not been defined during the development of the component, it is not available at installation and runtime times.
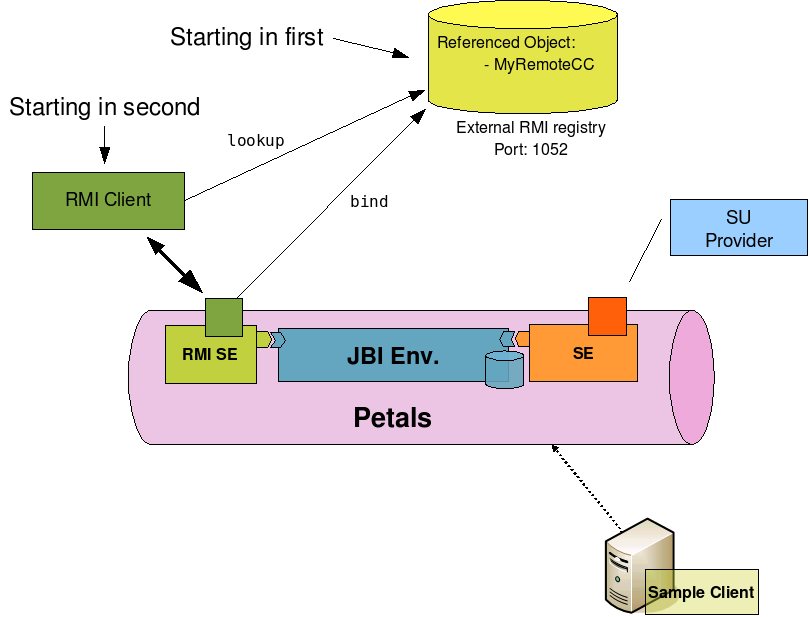
Using an external RMI registry
If the component is configured to have an external RMI registry (the parameter 'embeddedregistry' is set to false), this external registry must be started before installation: